04第二章基本语法_流程控制
输入
从键盘获取不同类型的变量,需要使用Scanner类
使用步骤:
- 导包:import java.util.Scanner;
- 实例化:Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- 使用Scanner相关类,获取指定类型的变量。
- int nextInt()
- String next()
- String nextLine()
需要根据相应的方法,来输入指定类型的值,如果输入的数据类型和要求的类型不匹配,会导致程序报错终止
/**
输入类Scanner
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int data = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(data);
}
}
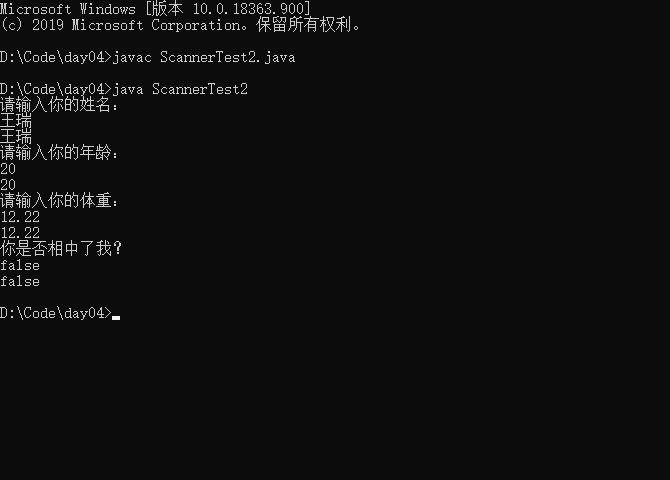
- 练习,征婚录入系统
//第一步
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerTest2{
public static void main(String[] args){
//第二步创建对象
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
String name = scan.next();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println("请输入你的年龄:");
int age = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println("请输入你的体重:");
double weight = scan.nextDouble();
System.out.println(weight);
System.out.println("你是否相中了我?");
boolean isLove = scan.nextBoolean();
System.out.println(isLove);
}
}
运行结果:
流程控制
三种基本流程结构:
- 顺序结构:程序从上到下逐行执行,中间没有任何判断和跳转。
- 分支结构:根据条件,选择性的执行某段代码,有
if...else和switch-case两种分支语句。 - 循环结构:根据循环条件,重复性的执行某段代码。有
while、do...while、for三种
分支结构
if-else结构
-
第一种:
if(判断条件){ 表达式 } -
第二种:
if(判断条件){ 表达式 }else{ 表达式 } -
第三种:
if(判断条件){ 表达式 }else if(判断条件){ 表达式 }else{ 表达式 } -
if-else结构是可以相互嵌套的
-
如果if-else结构中的执行语句只有一行,对应的{}可以省略,但是不建议省略。
/*
判断
*/
public class IfTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int age = 14;
//第一种
if(age <18){
System.out.println("未成年禁止入内");
}
//第二种:二选一
if(age<18){
System.out.println("未成年人禁止入内");
}else{
System.out.println("客官您里面请");
}
//第三种:n选一
if(age <14){
System.out.println("儿童");
}else if(age <18){
System.out.println("青少年");
}else if(age < 30){
System.out.println("奋斗之年");
}else{
System.out.println("而立之年");
}
}
}
switch-case结构
- 格式:
switch(表达式){
case 常量:
执行语句;
break;
case 常量:
执行语句;
break;
default:
执行语句;
}
- 总结:
- 根据switch表达式中的值,一次匹配各个case中的常量,一旦匹配成功,则进入相应的case结构,调用其执行语句。当调用完执行语句后,则仍然向下继续执行其他case结构中的执行语句,知道遇到break关键词或次switch-case机构末尾结束为止。
- break,可以使用在switch-case结构中,表示一旦执行到此关键字,就会跳出switch-case结构。
- switch结构中的表达式,只能是如下6种类型之一:
byte、short、char、int、枚举类型、String。 - case 后面只能声明常量。不能声明范围。
- break关键字是可选的。
- default:相当与if-else结构中的else,是可选的。
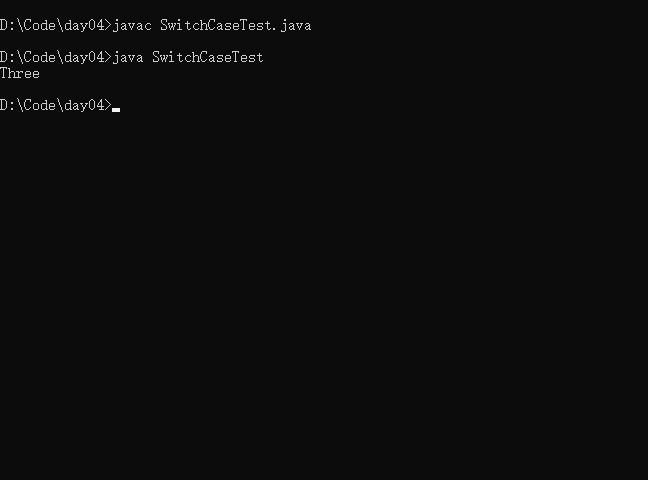
- 实例1
/*
switch-case结构
*/
public class SwitchCaseTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int number = 3;
switch(number){
case 0:
System.out.println("Zero");
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("One");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Two");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Three");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Four");
break;
}
}
}
- 实例2 使用switch对学生成绩大于60分的,输出“合格”,低于60分的,输出“不合格”
/*
switch-case结构实例
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseExer{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = scan.nextInt() / 10;
switch(number){
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:
System.out.println("合格");
break;
default:
System.out.println("不合格");
break;
}
}
}
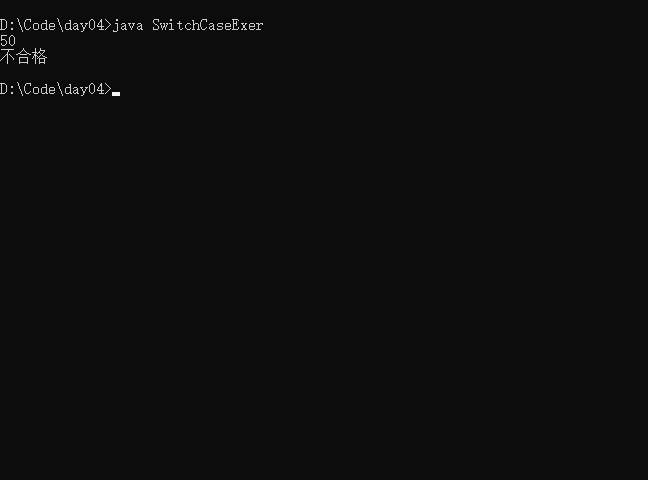
说明:如果多个case执行语句是一样的,可以进行合并
- 实例3 根据月份,打印月数所属的季节。
/*
switch-case结构实例,根据月份,打印月数所属的季节
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseExer2{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入月份:");
int month = scan.nextInt() ;
switch(month){
case 12:
case 1:
case 2:
System.out.println("冬季");
break;
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("春季");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
System.out.println("夏季");
break;
case 9:
case 10:
case 11:
System.out.println("秋季");
break;
default:
System.out.println("月份输入错误");
}
}
}
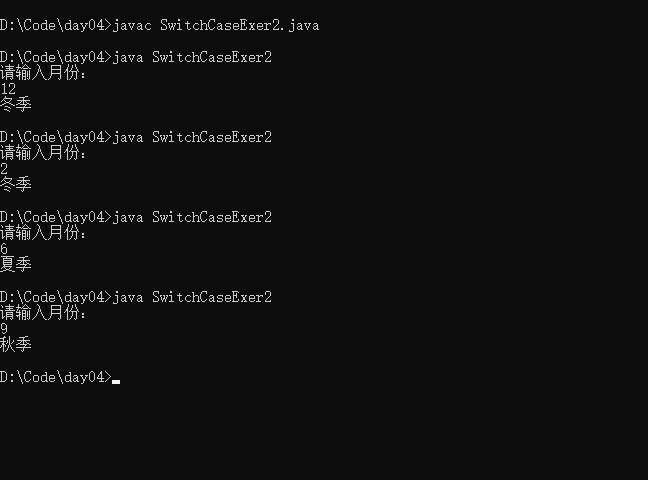
- 实例4 编写程序:从键盘上输入2019年的“month”和“day”,要求通过程序 输出输入的日期为2019年的第几天。
/*
switch-case
从键盘上输入2019年的“month”和“day”,要求通过程序 输出输入的日期为2019年的第几天
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseExer3{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入月份:");
int month = scan.nextInt() ;
System.out.println("请输入日子:");
int day = scan.nextInt() ;
int result = 0;
switch(month){
case 12:
result += 30;
case 11:
result += 31;
case 10:
result += 30;
case 9:
result += 31;
case 8:
result += 31;
case 7:
result += 30;
case 6:
result += 31;
case 5:
result += 30;
case 4:
result += 31;
case 3:
result += 28;
case 2:
result += 31;
case 1:
result += day;
}
System.out.println("2019年"+month+"月"+day+"日共计:"+result+"天");
}
}
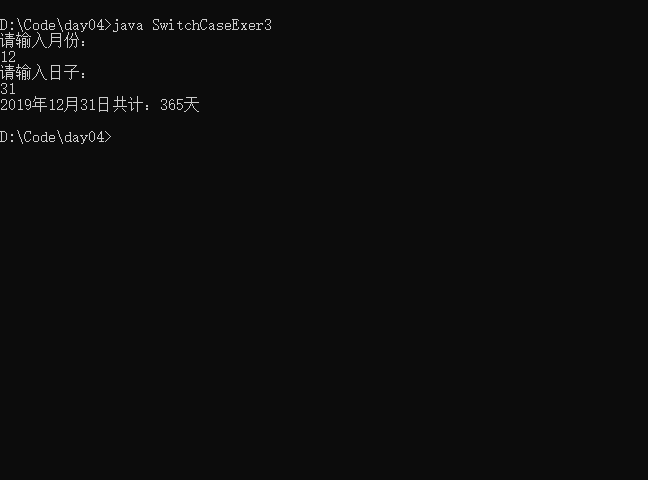
说明break是可选的,可以不添加
分支结构的选择
- 凡是可以使用switch-case的结构,都可以转换为if-else;反之不成立。
- 凡是可以使用switch-case(case取值不太多)或if-else结构的,我们优先使用switch-case。
循环结构
在默写特定满足条件的情况下,反复执行特定代码的功能。
- 循环语句的分类
- for循环
- while循环
- do-while循环
- 循环结构的4要素:
- ①初始化条件
- ②循环条件 -->boolean类型
- ③循环体
- ④迭代条件
for循环
- 格式:
for(①;②;④){
③
}
abcbcbc
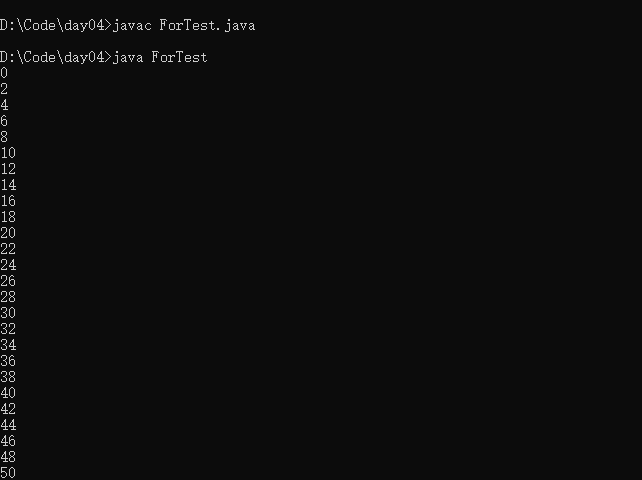
- 练习 遍历100以内的偶数
public class ForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 0;i <= 100;i++){
if(i % 2 == 0)
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
- 练习2 编写程序从1循环到150,并在每行打印一个值,另外在每个3的倍数行 上打印出“foo”,在每个5的倍数行上打印“biz”,在每个7的倍数行上打印 输出“baz”
public class ForExer{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 150 ; i++ ){
String result = i + " ";
if(i % 3 == 0)
result += "foo ";
if(i % 5 == 0)
result += "biz ";
if(i % 7 == 0)
result += "baz";
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}

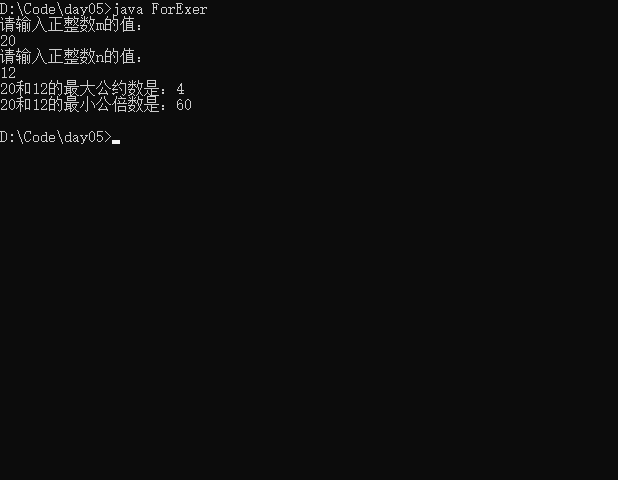
- 练习3 输入两个正整数,m和n,求最大公约数和最小公倍数。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ForExer{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入正整数m的值:");
int m = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入正整数n的值:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
//最大公约数
for(int i = (m>n?n:m);i>0;i--){
if(m%i==0 && n%i==0){
System.out.println(m+"和"+n+"的最大公约数是:"+i);
break;
}
}
//最小公倍数
for(int i = 1;i<=(m>n?m:n);i++){
if(i*m % n == 0){
System.out.println(m+"和"+n+"的最小公倍数是:"+i*m);
break;
}
}
}
}
while循环
结构:
初始化条件;
while(判断条件){
循环体;
迭代条件;
}
说明:
- 不要忘记写迭代条件,可能会导致程序死循环.
- 我们写程序,要避免出现死循环。
- for循环和while循环是可以相互转换的。
- 区别:for和while循环的初始化条件的作用范围不同。
public class WhileTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i = 1;
while(i<=100){
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
}
i++;
}
}
}

do-while循环
格式:
初始化条件;
do{
循环体;
迭代条件;
}while(判断条件);
说明:
- do-while无论条件符不符合都至少执行一次
public class DoWhileTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
//求100以内偶数的和以及数量。
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
do{
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
count++;
sum += i;
}
i++;
}while(i<=100);
System.out.println("100以内偶数的数量是"+count+",和是"+sum);
}
}
嵌套循环
- 一般来说,循环嵌套不会超过3层。
- 解释:讲一个循环结构A声明在另一个循环结构B的循环体中,就构成了嵌套循环。
- 外层循环:循环结构B
- 内层循环:循环结构A
- for,while,do-while都可以做为外层或内层循环。
实例:每次打印一颗*,打印如下内容:
******
******
******
******
******
public class ForForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++){
for(int j = 0;j < 6 ; j++){
System.out.print('*');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
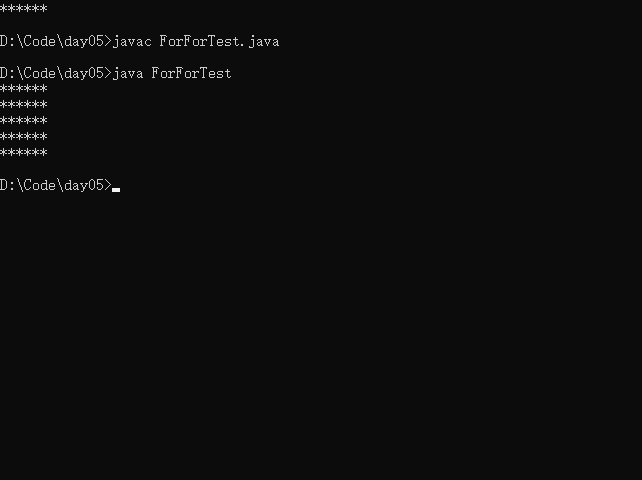
说明:
- 内层循结构遍历的一遍,相当与外层结构循环体执行了一次。
- 假设外层循环m和内层循环n次,那么内层循环总共执行了m*n次。
实例2:每次打印一颗*,打印如下内容:
*
**
***
****
*****
public class ForForTest2{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++){
for(int j = 0;j < i ; j++){
System.out.print('*');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
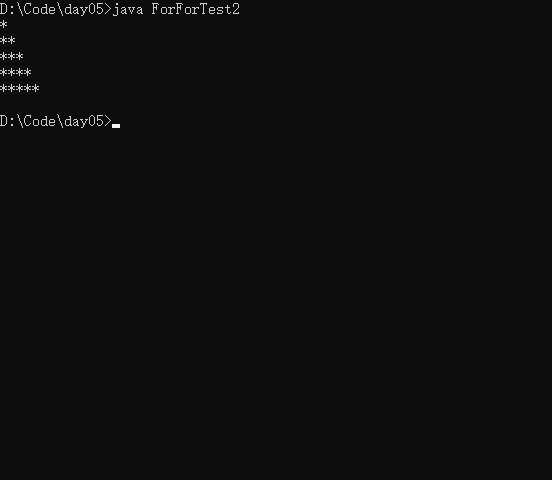
综合练习题
从键盘读入个数不确定的整数,并判断正数和负数的个数,输入为0时结束程序。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ForWhileExer{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scann = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean bool = true;
int zheng = 0;
int fu = 0;
while(bool){
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int data = scann.nextInt();
if(data ==0){
break;
}else if(data<0){
fu++;
}else{
zheng++;
}
}
System.out.println("正数个数"+zheng+";负数个数"+fu);
}
}
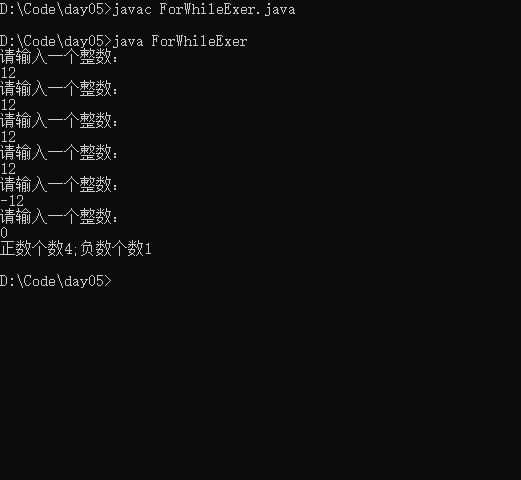
也可以使用:
for(;;){//参数都写空
}
说明:
1,. 不在循环条件部分限制次数的结构:for(;;)或while(ture)
九九乘法表
public class JiuJiuTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 1 ; i <=9 ; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){
System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+(i * j)+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
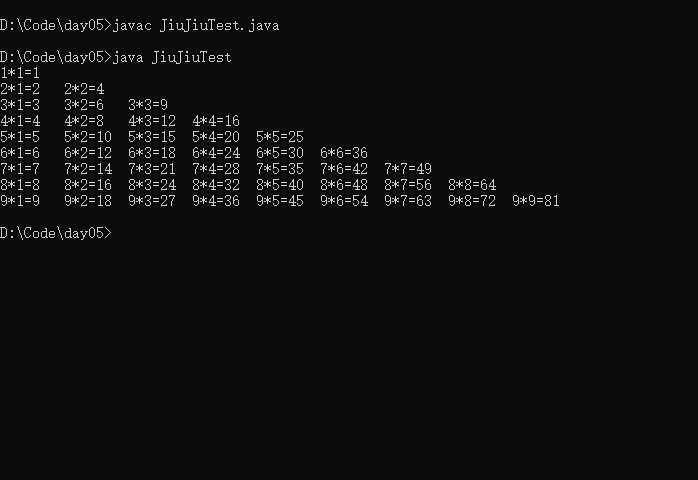
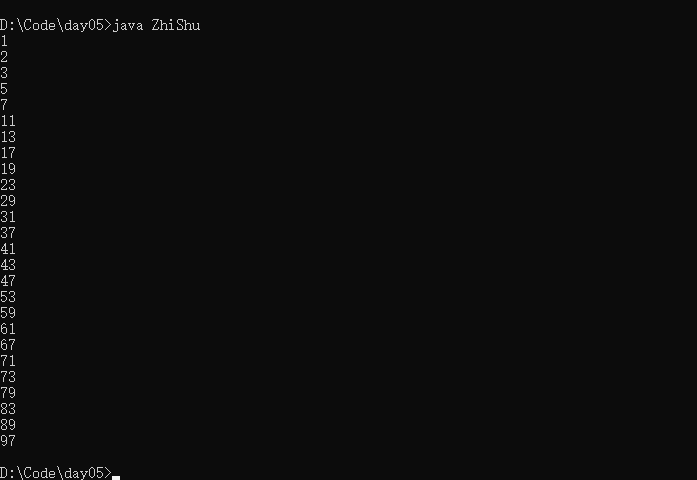
一百以内所有的质数
public class ZhiShu{
public static void main(String[] args){
boolean isFlag = true;
for(int i = 1;i<=100;i++){
for(int j = 1 ; j < i ; j++ ){
if(isFlag && i%j == 0 && j != 1){
isFlag = false;
}
}
if(isFlag){
System.out.println(i);
}
isFlag = true;
}
}
}
优化效率:10w以内的质数
public class ZhiShu2{
public static void main(String[] args){
boolean isBool = true;
int count = 0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 1;i <= 100000;i++){
//for(int j = 1; j < i; j++){
for(int j = 1; j <= Math.sqrt(i); j++){//优化2:不需要遍历到每个数量,只需要测试到开平方的数值即可
if(i % j == 0 &&j != 1){
isBool = false;
break;//优化1,添加break,当知道不是偶数的时候跳出内层for循环
}
}
if(isBool){
count++;
//System.out.println(i);
}
isBool = true;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共计质数:"+count+"个");
System.out.println("共计耗时:"+(end - start)+"毫秒");
}
}
-
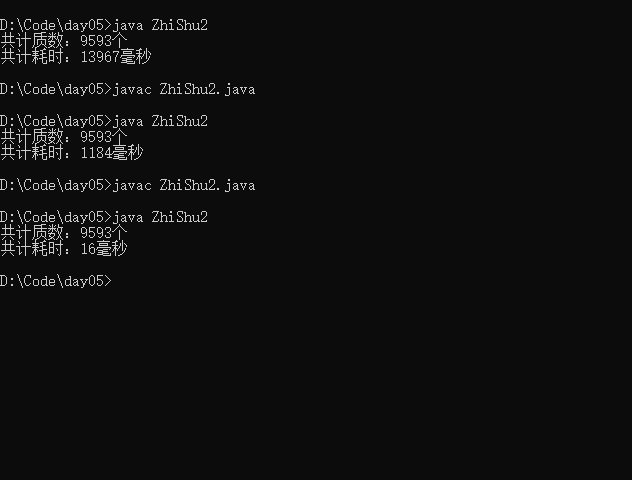
查看执行效率:
- 不优化:共计耗时:11405毫秒
- 优化1: 共计耗时:1275毫秒
- 优化2: 共计耗时:227毫秒
-
如果取消输出打印,会更快:
- 不优化:共计质数:9593个,共计耗时:13967毫秒
- 优化1: 共计质数:9593个,共计耗时:1184毫秒
- 优化2: 共计质数:9593个,共计耗时:16毫秒
特殊关键字break、continue
| 名称 | 使用范围 | 不同点 | 相同点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| break | switch-case、循环结构 | 结束当前循环 | 关键字后面不能声明执行语句 |
| continue | 循环结构中 | 结束当次循环 | 关键字后面不能声明执行语句 |
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
lab:for(int i = 1 ; i < 5 ; i++){
for(int j = 1 ; j < 10 ; j++){
if(j%4 == 0){
//break;//123 123 123 123(默认跳出当前for循环)
//continue;//1235679 1235679 1235679 1235679(默认结束当前本次for循环)
//break lab;//123
continue lab;//123123123123
}
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
说明:for循环前面可以加标签(例如lab),break或continue后面加上标签名(lab),可以结束或者跳过待标签(lab)的循环
DAY04问题
-
switch后面使用的表达式可以是哪些数据类型。
- byte、short、char、int、枚举类型、String
-
使用switch语句改写下列if语句
-
谈谈你对三元运算符、if-else和switch-case结构使用场景的理解。
- 都有分支的意思
- 能够使用三元运算符或switch-case的优先使用他俩,效率高。
- 能用三元表示的一定可以用if-else表示,反之不成立。
- 能用switch-case表示的一定可以用if-else表示,反之不成立。
-
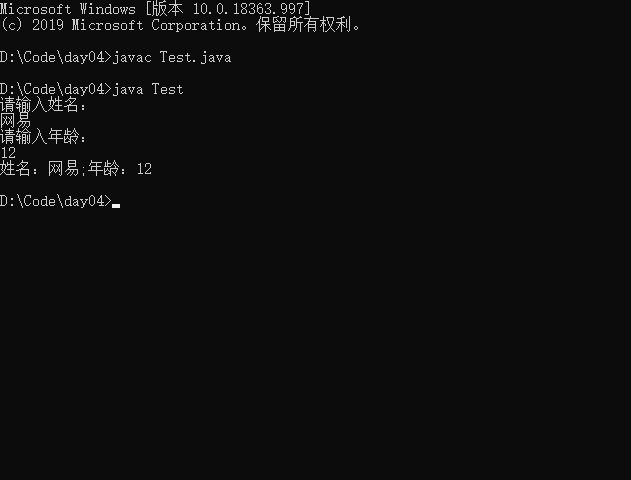
如果从控制台获取String和int类型的变量,并输出?使用代码实现。
//导包
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
//实例化对象
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
String name = scan.next();
System.out.println("请输入年龄:");
int age = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("姓名:"+name +";年龄:"+age);
}
}
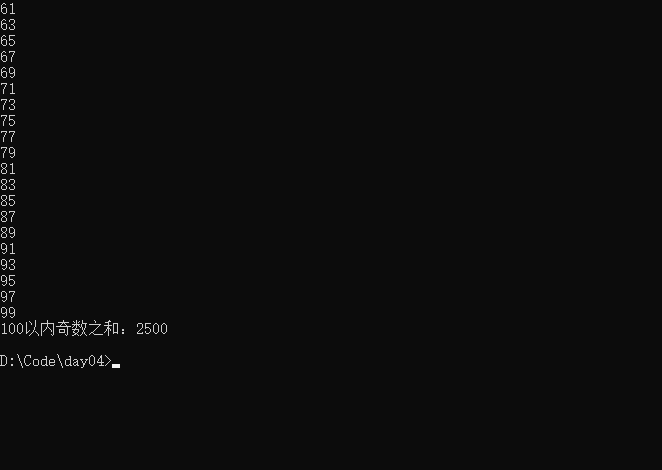
- 使用for循环遍历100以内的奇数,并计算所有技术的和并输出。
public class ForExer2{
public static void main(String[] args){
int result = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <=100;i++){
if(i % 2 != 0){
result += i;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
System.out.println("100以内奇数之和:"+result);
}
}